BCS - Breast-Conserving Surgery

BCS - Breast-Conserving Surgery
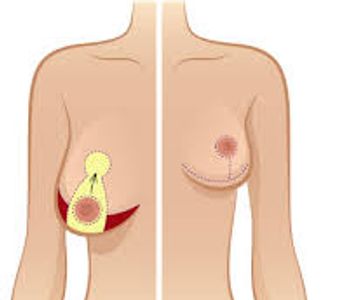
Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) removes the cancer while leaving as much normal breast as possible. Usually, some surrounding healthy tissue and lymph nodes also are removed. Breast-conserving surgery is sometimes called lumpectomy, quadrantectomy, partial mastectomy, or segmental mastectomy depending on how much tissue is removed.
Who Can Have Breast-Conserving Surgery (BCS)?
Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) is a treatment in which the cancerous lump and a rim of normal tissue are removed, but most of the breast is preserved.
It is a good option for many women with early-stage breast cancer.
Most patients who undergo BCS will also need radiation therapy afterward to reduce the risk of cancer coming back in the same breast.
Women who have a mastectomy (complete removal of the breast) for early-stage cancer are usually less likely to need radiation, but some may still be referred to a radiation oncologist, depending on individual case details.
Mastectomy Surgery
Mastectomy Surgery
A mastectomy is the surgical removal of one or both breasts, typically to treat or prevent breast cancer. Various types exist, from a simple mastectomy that removes all breast tissue to more specialized procedures like a skin-sparing mastectomy or nipple-sparing mastectomy, which preserve more skin for reconstruction. Other tissues, such as lymph nodes or chest wall muscles, may also be removed depending on the cancer's extent.
Types of Mastectomy
Simple (Total) Mastectomy
- Removes the entire breast, including nipple and areola.
- Lymph nodes and chest muscles are not removed.
- Recommended for DCIS or early-stage cancers not suitable for breast-conserving surgery.
Modified Radical Mastectomy (MRM)
- Removes the entire breast along with axillary (underarm) lymph nodes.
- Chest muscles are preserved.
- Commonly done for invasive breast cancer to check lymph node spread.
Radical Mastectomy (Halsted’s)
- Removes the breast, lymph nodes, and chest wall muscles.
- Rarely performed now — only used in very advanced cases involving chest muscles.
Skin-Sparing Mastectomy
- Removes breast tissue but preserves most of the overlying skin.
- Ideal when immediate breast reconstruction is planned.
- Provides a better cosmetic result.
Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy
- The entire breast tissue is removed but the nipple and areola are preserved.
- Suitable for selected early-stage cancers or preventive mastectomies.
- Offers the most natural appearance after reconstruction.
Reasons for a mastectomy
- To treat breast cancer: It is a common treatment for many types and stages of breast cancer.
- To prevent breast cancer: It can be a preventive measure for individuals with a very high risk of developing breast cancer, such as those with a family history or a mutation in genes like BRCA1 or BRCA2.
- To prevent cancer in the other breast: A contralateral prophylactic mastectomy removes the healthy breast in a person who has breast cancer in the other breast.

Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy - SNB
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy - SNB
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SNB) is a precise and minimally invasive procedure used to check whether breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
🌸 What Are Lymph Nodes and Why Are They Important?
The lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands that play a vital role in your body’s immune system. In breast cancer, cancer cells can sometimes travel from the breast to nearby lymph nodes — most commonly in the axilla (underarm). Knowing whether these nodes contain cancer cells is essential for:
- Deciding the stage of cancer
- Planning treatment
- Predicting prognosis
🎯 What is a Sentinel Lymph Node?
The sentinel lymph node is the first lymph node (or group of nodes) that directly receives drainage from the breast tumor area. If cancer spreads from the breast, it would first reach this node. Therefore, checking the sentinel node tells us whether cancer has begun to spread beyond the breast.
🩺 What is Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SNB)?
SNB is a surgical test in which only a few key lymph nodes — the sentinel nodes — are identified and removed for examination. If these nodes are cancer-free, it is very likely that the other lymph nodes are also unaffected. This allows the surgeon to avoid removing all the lymph nodes, minimizing complications like arm swelling (lymphedema).

Axillary Dissection - A.D.
Axillary Dissection - A.D.
Axillary Dissection (A.D.), also known as Axillary Lymph Node Dissection (ALND), is a surgical procedure performed to remove lymph nodes from the underarm (axilla) to determine whether breast cancer has spread beyond the breast.
🌸 Why Are Axillary Lymph Nodes Important?
The lymphatic system is part of the body’s natural defense mechanism.
Cancer cells from the breast may sometimes travel to the axillary lymph nodes first before spreading to other parts of the body.
Assessing these nodes helps your doctor:
- Understand the stage of breast cancer
- Plan the best treatment approach
- Predict the prognosis (outcome)
⚙️ Indications for Axillary Dissection
Axillary dissection is recommended when:
- Cancer is detected in lymph nodes (by biopsy or sentinel node biopsy)
- Multiple sentinel lymph nodes are positive for cancer
- Large or locally advanced breast cancer is present
- Recurrent or residual cancer after previous surgery
🩷 It may also be performed when sentinel node biopsy is not possible or available.

Oncoplasty

Oncoplasty
Oncoplastic Breast Surgery (Oncoplasty) is an advanced surgical technique that combines oncologic (cancer removal) surgery with plastic (reconstructive) surgery.
It ensures complete cancer removal without compromising the shape, size, or appearance of the breast.
Advantages of Oncoplastic Surgery
✅ Ensures complete cancer removal with clear margins
✅ Maintains breast shape and appearance
✅ Reduces need for mastectomy in many cases
✅ Enhances self-image and confidence
✅ Allows one-stage reconstruction — no need for multiple surgeries
✅ Can be combined with radiation therapy post-surgery
RECONSTURCTION SURGERY

RECONSTRUCTION SURGERY
Reconstruction Breast Surgery
Reconstructive surgery repairs parts of your body affected by defects you were born with, defects that have developed because of disease, or defects caused by an injury. Cleft lip and palate repair and breast reconstructions are examples of reconstructive surgery.
The word “reconstructive” means to rebuild after something has been damaged or destroyed.
Perforator Flap : Perforator flap surgery is a reconstructive technique that uses tissue with its own blood supply to repair a defect elsewhere in the body, without sacrificing the underlying muscle. This approach minimizes damage at the donor site and is used for various reconstructions, such as breast, head, and neck reconstruction. The "perforator" is the blood vessel that passes through a muscle or septum to reach the flap tissue, and the type of flap is named after this vessel.
LD Flap : An LD flap (latissimus dorsi flap) is a reconstructive surgery that uses a patient's own tissue from the back to rebuild a breast or cover a defect on the torso. It involves transferring the latissimus dorsi muscle, along with its overlying skin and fat, from the back to the chest while keeping it connected to its blood supply, or as a free flap with microsurgical connection. It is often combined with a breast implant or tissue expander to achieve the desired volume, as the back tissue alone may be insufficient.
FREE Flap : Free flap surgery, also known as microvascular reconstruction, is a complex reconstructive surgery that involves transferring tissue from one part of the body to another to repair defects from trauma, cancer removal, or other conditions. During the procedure, the blood vessels of the transplanted tissue (the flap) are completely detached from their original location and then surgically reconnected to blood vessels at the defect site, typically using a microscope. This allows the transplanted tissue, which can include skin, bone, muscle, fat, and nerves, to receive a new blood supply and survive.
WIDE LOCAL EXCISION (benign tumor)
WIDE LOCAL EXCISION - BENIGN TUMOR
Wide Local Excision, also called lumpectomy or breast-conserving surgery, is a procedure in which a breast lump or cancer is removed along with a small margin of healthy tissue, while preserving the rest of the breast.
It is commonly recommended for early-stage breast cancer and selected benign breast lumps. The surgery helps maintain breast shape and offers good cosmetic results. In cancer cases, radiotherapy is usually advised after WLE to reduce the risk of recurrence.
When is Wide Local Excision recommended?
WLE is commonly advised in:
- Early-stage breast cancer
- Small, localized tumors
- Benign breast lumps (fibroadenoma, phyllodes tumor) when large or symptomatic
- Patients suitable for breast-conserving surgery
How is the procedure done?
- The surgery is performed under general anesthesia
- Only the lump and a margin of normal tissue are removed
- The breast shape is preserved as much as possible
- In cancer cases, sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary surgery may be done simultaneously
- The removed tissue is sent for histopathological examination
Advantages of Wide Local Excision
- Preserves most of the breast
- Good cosmetic outcome
- Shorter recovery time
- Less extensive surgery compared to mastectomy
- Effective cancer control when combined with radiotherapy.

Incision and Drainage (I&D) of Abscess BREAST SURGERY

I &D of Abscess
Incision and Drainage (I&D) of Abscess
Incision and Drainage (I&D) is a minor surgical procedure performed to treat an abscess — a painful, swollen lump filled with pus caused by infection.
What Is an Abscess?
An abscess is a localized collection of pus under the skin or inside the breast tissue.
It usually occurs due to:
- Bacterial infection (commonly Staphylococcus aureus)
- Blocked ducts or injured skin
- Breastfeeding-related infections (lactational abscess)
If left untreated, an abscess can enlarge, become more painful, or lead to spreading infection.
Microductectomy
Microductectomy
Microductectomy (Duct Excision Surgery)
Microductectomy — also known as Single Duct Excision or Minor Duct Excision — is a short surgical procedure used to remove a single milk duct from the breast. It is most commonly performed to diagnose and treat nipple discharge, especially when the discharge is bloody, persistent, or coming from one duct only.
When Is Microductectomy Recommended?
Your doctor may recommend microductectomy if you have:
- Nipple discharge that is spontaneous, persistent, or blood-stained
- Discharge from a single duct (usually one opening on the nipple)
- Normal imaging (mammogram/ultrasound) but ongoing symptoms
- Suspicion of a small benign growth like intraductal papilloma or ductal lesion
It is both diagnostic and therapeutic — the procedure removes the abnormal duct and also helps confirm the underlying cause through pathology testing.
Aftercare and Recovery
- A light dressing is applied for 2–3 days.
- Mild discomfort, bruising, or swelling may occur for a few days.
- Pain relief and antibiotics are prescribed.
- You can usually return to normal activities within 2–3 days.
- Avoid pressure or tight clothing on the operated area for a week.
- The final biopsy report is typically available within 5–7 days.
Benefits of Microductectomy
✅ Eliminates the cause of nipple discharge
✅ Provides definitive diagnosis through histopathology
✅ Minimally invasive with excellent cosmetic outcome
✅ Usually no impact on breast shape or future breastfeeding
✅ Short recovery and minimal downtime

Total Duct Excision

Total Duct Excision
Total Duct Excision (TDE)
Total duct excision is a surgical procedure to remove all major milk ducts from behind the nipple to diagnose and treat persistent nipple discharge. The removed tissue is sent for a biopsy to determine the cause, which can range from benign conditions like duct ectasia to, less commonly, malignancy. This operation is performed to stop the discharge and provide a definitive diagnosis, especially when symptoms are concerning.
Why Is Total Duct Excision Done?
Your breast surgeon may recommend TDE if you have:
- Nipple discharge from several ducts (often both clear or blood-stained)
- Recurrent discharge even after previous microductectomy
- Non-diagnostic imaging but ongoing symptoms
- Papillomatosis, duct ectasia, or chronic infection of the ducts
- Suspicion of underlying intraductal lesions on duct imaging
TDE is both diagnostic and therapeutic — it removes the diseased ducts and provides tissue for pathology analysis to rule out cancer or other abnormalities.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Dressing: Light dressing kept for 2–3 days
- Pain: Mild discomfort or swelling for a few days
- Antibiotics & pain relief will be prescribed
- Normal activities: Usually resume in 3–5 days
- Follow-up: Suture removal (if required) after about a week
- Breastfeeding: Future breastfeeding from the operated breast is not possible, as the milk ducts are removed
Benefits of Total Duct Excision
✅ Permanently treats persistent or bothersome nipple discharge
✅ Provides definitive diagnosis when imaging is inconclusive
✅ Cosmetically hidden scar at the edge of the areola
✅ Short, safe, and effective day-care surgery
✅ Prevents repeated infections and anxiety about discharge
Breast AUGMENTATION Surgery

Augmentation
Breast Augmentation
(Breast Enlargement Surgery)
Breast Augmentation, also known as Augmentation Mammaplasty, is a cosmetic surgical procedure that enhances the size, shape, and fullness of the breasts using breast implants or fat transfer.
Why Women Choose Breast Augmentation
Women may consider breast augmentation for several reasons, including:
- Naturally small or underdeveloped breasts
- Loss of breast volume after pregnancy, breastfeeding, or weight loss
- To restore symmetry if one breast is smaller than the other
- To enhance body proportion or confidence
- As reconstruction after breast cancer surgery
Whatever the reason, the goal is always the same — to help you feel confident, feminine, and natural in your body.
Types of Breast Augmentation
Implant-Based Augmentation
Breast implants are inserted behind the breast tissue or chest muscle.
Types of implants include:
- Silicone implants – soft, natural feel and appearance
- Saline implants – filled with sterile salt water
- Anatomical (teardrop) or round shapes based on desired contour
Fat Transfer Augmentation
Your own fat is taken from areas like the abdomen or thighs (via liposuction), purified, and then injected into the breasts.
✅ No foreign material
✅ Natural look and feel
✅ Ideal for mild to moderate enhancement
Benefits of Breast Augmentation
✅ Improved breast shape, volume, and contour
✅ Enhanced body confidence and posture
✅ Natural and long-lasting results with modern implants
✅ Safe and customizable according to individual needs
✅ Minimal visible scarring and quick recovery
Breast Reduction Surgery
Breast Reduction Surgery
Breast reduction surgery, or reduction mammoplasty, is a procedure to remove excess breast tissue, fat, and skin to create smaller, more proportionate breasts and relieve physical pain like back, neck, and shoulder pain. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, and techniques vary based on the amount of reduction needed. After surgery, a recovery period of two to three weeks is needed to return to normal activities, and a full recovery can take two to three months
Benefits:
- Improved posture and comfort
- Easier physical activity
- Enhanced body symmetry
- Boosted confidence
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses powerful anti-cancer medications (cytotoxic drugs) given by mouth or intravenously to treat breast cancer. It is an essential component of multi-modality breast cancer treatment.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells in the breast, chest wall and sometimes adjacent lymph nodes. It complements surgery and other treatments to reduce the risk of recurrence and improve long-term outcomes.
When is it used?
Radiation therapy may be recommended in several situations:
- After breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) to treat the remaining breast tissue and reduce the chance of the cancer coming back in the same breast.
- After a mastectomy, especially if the tumour was large, or lymph nodes were involved, or margins were close/positive.
- To treat the chest wall and/or regional lymph nodes (under the arm, above the collarbone) when needed.
- Less commonly, to shrink a tumour before surgery (neoadjuvant) or to help relieve symptoms when cancer has spread.
HORMONAL TREATMENT
Balancing Hormones for Breast Health
Hormonal therapy plays a vital role in the management of hormone-responsive breast conditions — both benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (breast cancer). Under the expert care of Dr. Swati Suradkar, patients receive a precise, personalized approach designed to restore hormonal balance, reduce symptoms, and prevent recurrence.
What Is Hormonal Therapy?
Hormonal (endocrine) therapy works by blocking or reducing the effect of estrogen and progesterone, hormones that can stimulate the growth of certain breast cells or cancers. It can be used as:
- Primary treatment for hormone receptor–positive breast cancer.
- Adjuvant therapy after surgery, to lower the risk of cancer returning.
- Preventive therapy for high-risk individuals.
- Symptom control for hormonal breast conditions such as fibrocystic changes, mastalgia (breast pain), or cyclical swelling.
Common Hormonal Treatments
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) – e.g., Tamoxifen, which blocks estrogen’s action on breast tissue.
- Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs) – e.g., Letrozole, Anastrozole, Exemestane; reduce estrogen production in post-menopausal women.
- Ovarian Suppression Therapies – e.g., injections or surgery to stop estrogen production in pre-menopausal women.
- Hormonal Balance Medications – for benign breast disorders, to relieve pain, swelling, or tenderness caused by hormonal fluctuations.
Benefits of Hormonal Treatment
- Reduces the risk of breast cancer recurrence.
- Slows or stops growth of hormone-positive tumours.
- Manages pain and discomfort in benign breast conditions.
- Offers a non-surgical, targeted approach for many patients.
Targeted Breast Treatment Therapy
Precision Medicine for Breast Cancer
Targeted therapy is an advanced form of breast cancer treatment that specifically attacks cancer cells while sparing most normal, healthy cells. Unlike chemotherapy, which affects all rapidly dividing cells, targeted drugs focus on the unique molecular changes that drive breast cancer growth.
Under the guidance of Dr. Swati Suradkar, patients receive precise, evidence-based care plans designed according to their tumour’s genetic and molecular profile — ensuring the best possible outcomes with fewer side effects.
What Is Targeted Therapy?
Targeted therapy works by identifying and blocking the specific pathways or receptors that help breast cancer cells grow, divide, or spread. Before starting treatment, special tests (such as HER2, ER/PR, or genomic profiling) are performed to determine whether your cancer will respond to these medications.
Immuno Therapy
Harnessing the Power of the Immune System to Fight Cancer
Immunotherapy is an innovative form of treatment that helps your body’s own immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively. It represents a major advancement in modern breast cancer care — offering new hope for patients with certain aggressive or advanced cancers.
Under the expert supervision of Dr. Swati Suradkar, patients receive a carefully tailored treatment plan combining surgery, targeted drugs, chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy as needed — ensuring the most effective and personalized care possible.
What Is Immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy works by stimulating the immune system or removing the “brakes” that prevent it from attacking cancer cells. It helps the body identify cancer as a threat and destroy it, without harming normal, healthy cells.
It is especially beneficial for patients with:
- Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
- Locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer
- Cancers that express PD-L1 (Programmed Death Ligand-1)
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.